Building a Vue CRUD App with a .NET API
CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations are the backbone of most web applications. In this article, we'll guide you through building a CRUD app using Vue on the front end and a .NET API on the back end, showcasing how these technologies integrate to create a powerful full-stack solution.
Prerequisites
- Node.js
- .NET 8
- MySQL
Setup Vue project
npm create vite@4.4.0 view -- --template vue
cd view
npm install vue-router@4 axiosVue project structure
├─ index.html
├─ public
│ └─ css
│ └─ style.css
└─ src
├─ App.vue
├─ components
│ └─ product
│ ├─ Create.vue
│ ├─ Delete.vue
│ ├─ Detail.vue
│ ├─ Edit.vue
│ ├─ Index.vue
│ └─ Service.js
├─ http.js
├─ main.js
└─ router.jsVue project files
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')This main.js file is the entry point for a Vue.js application. It sets up and mounts the app with routing by importing the root component and router, creating the app instance, and configuring it with the router before mounting it to the #app element.
App.vue
<template>
<router-view />
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>This App.vue file defines the root component of a Vue.js application. It uses a <router-view />
router.js
import { createWebHistory, createRouter } from 'vue-router'
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/product'
},
{
path: '/product',
name: 'product',
component: () => import('./components/product/Index.vue')
},
{
path: '/product/create',
component: () => import('./components/product/Create.vue')
},
{
path: '/product/:id/',
component: () => import('./components/product/Detail.vue')
},
{
path: '/product/edit/:id/',
component: () => import('./components/product/Edit.vue')
},
{
path: '/product/delete/:id/',
component: () => import('./components/product/Delete.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes,
})
export default routerThis router.js file configures routing for a Vue.js application. It sets up routes for various product-related views, including listing, creating, editing, and deleting products, as well as a default redirect to the product list. The router uses `createWebHistory` for HTML5 history mode and exports the configured router instance.
http.js
import axios from 'axios'
let http = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://localhost:5122/api',
headers: {
'Content-type': 'application/json'
}
})
export default httpThe http.js file configures and exports an Axios instance with a centralized base URL, which is a standard practice for managing API endpoints and default headers set to application/json.
Create.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form method="post" @submit.prevent="create()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input id="product_name" name="Name" class="form-control" v-model="product.name" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input id="product_price" name="Price" class="form-control" v-model="product.price" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<router-link class="btn btn-secondary" to="/product">Cancel</router-link>
<button class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Service from './Service'
export default {
name: 'ProductCreate',
data() {
return {
product: {}
}
},
methods: {
create() {
Service.create(this.product).then(() => {
this.$router.push('/product')
}).catch((e) => {
alert(e.response.data)
})
}
}
}
</script>
This Create.vue component provides a form for adding a new product with fields for name and price. On submission, it calls a create method to save the product and redirects to the product list upon success. It also includes a cancel button to navigate back to the list and handles errors with an alert.
Delete.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form method="post" @submit.prevent="this.delete()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="Id" class="form-control" :value="product.id" type="number" required />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input readonly id="product_name" name="Name" class="form-control" :value="product.name" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input readonly id="product_price" name="Price" class="form-control" :value="product.price" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<router-link class="btn btn-secondary" to="/product">Cancel</router-link>
<button class="btn btn-danger">Delete</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Service from './Service'
export default {
name: 'ProductDelete',
data() {
return {
product: {}
}
},
mounted() {
this.get()
},
methods: {
get() {
return Service.delete(this.$route.params.id).then(response => {
this.product = response.data
})
},
delete() {
Service.delete(this.$route.params.id, this.product).then(() => {
this.$router.push('/product')
}).catch((e) => {
alert(e.response.data)
})
}
}
}
</script>
The Delete.vue component provides a form for deleting a product, with read-only fields for the product's. The component fetches the product details when mounted. The form calls a delete method to remove the product and redirects to the product list upon success.
Detail.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form method="post">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="Id" class="form-control" :value="product.id" type="number" required />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input readonly id="product_name" name="Name" class="form-control" :value="product.name" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input readonly id="product_price" name="Price" class="form-control" :value="product.price" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<router-link class="btn btn-secondary" to="/product">Back</router-link>
<router-link class="btn btn-primary" :to="`/product/edit/${product.id}`">Edit</router-link>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Service from './Service'
export default {
name: 'ProductDetail',
data() {
return {
product: {}
}
},
mounted() {
this.get()
},
methods: {
get() {
return Service.get(this.$route.params.id).then(response => {
this.product = response.data
})
}
}
}
</script>
The Detail.vue component displays detailed information about a product. It features read-only fields for the product's. The component fetches product details when mounted. It includes a "Back" button to navigate to the product list and an "Edit" button to navigate to the product's edit page.
Edit.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form method="post" @submit.prevent="edit()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="Id" class="form-control" v-model="product.id" type="number" required />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input id="product_name" name="Name" class="form-control" v-model="product.name" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input id="product_price" name="Price" class="form-control" v-model="product.price" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<router-link class="btn btn-secondary" to="/product">Cancel</router-link>
<button class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Service from './Service'
export default {
name: 'ProductEdit',
data() {
return {
product: {}
}
},
mounted() {
this.get()
},
methods: {
get() {
return Service.edit(this.$route.params.id).then(response => {
this.product = response.data
})
},
edit() {
Service.edit(this.$route.params.id, this.product).then(() => {
this.$router.push('/product')
}).catch((e) => {
alert(e.response.data)
})
}
}
}
</script>
The Edit.vue component provides a form for editing an existing product. It includes fields for the product's. The component fetches the product details when mounted and updates the product on form submission. It also features a "Cancel" button to navigate back to the product list and a "Submit" button to save the changes.
Index.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Price</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="product in products" :key="product">
<td class="text-center">{{product.id}}</td>
<td>{{product.name}}</td>
<td class="text-center">{{product.price}}</td>
<td class="text-center">
<router-link class="btn btn-secondary" :to="`/product/${product.id}`" title="View"><i class="fa fa-eye"></i></router-link>
<router-link class="btn btn-primary" :to="`/product/edit/${product.id}`" title="Edit"><i class="fa fa-pencil"></i></router-link>
<router-link class="btn btn-danger" :to="`/product/delete/${product.id}`" title="Delete"><i class="fa fa-times"></i></router-link>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<router-link class="btn btn-primary" to="/product/create">Create</router-link>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Service from './Service'
export default {
name: 'ProductIndex',
data() {
return {
products: []
}
},
mounted() {
this.get()
},
methods: {
get() {
Service.get().then(response => {
this.products = response.data
}).catch(e => {
alert(e.response.data)
})
}
}
}
</script>
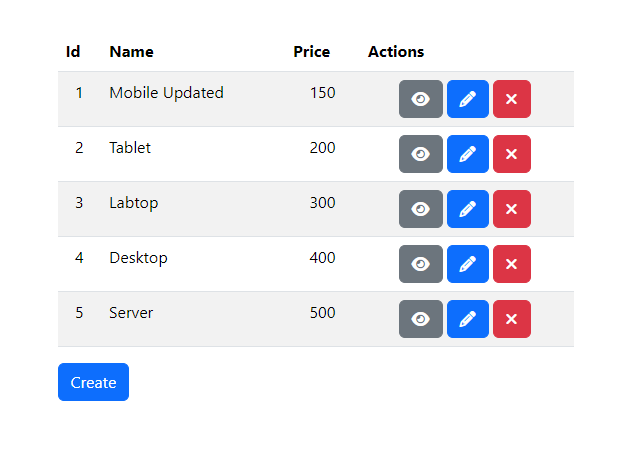
The Index.vue component displays a table of products with columns for ID, name, and price. It fetches the list of products when mounted and populates the table. Each product row includes action buttons for viewing, editing, and deleting the product. There is also a "Create" button for adding new products.
Service.js
import http from '../../http'
export default {
get(id) {
if (id) {
return http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
else {
return http.get('/products' + location.search)
}
},
create(data) {
if (data) {
return http.post('/products', data)
}
else {
return http.get('/products/create')
}
},
edit(id, data) {
if (data) {
return http.put(`/products/${id}`, data)
}
else {
return http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
},
delete(id, data) {
if (data) {
return http.delete(`/products/${id}`)
}
else {
return http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
}
}The Service.js file defines API methods for handling product operations. It uses an http instance for making requests:
get(id)Retrieves a single product by ID or all products if no ID is provided.create(data)Creates a new product with the provided data or fetches the creation form if no data is provided.edit(id, data)Updates a product by ID with the provided data or fetches the product details if no data is provided.delete(id, data)Deletes a product by ID or fetches the product details if no data is provided.
style.css
.container {
margin-top: 2em;
}
.btn {
margin-right: 0.25em;
}The CSS adjusts the layout by adding space above the container and spacing out buttons horizontally.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bootstrap/5.3.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.5.0/css/all.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="/css/style.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="module" src="/src/main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>The HTML serves as the main entry point for a Vue application. It includes Bootstrap for styling and Font Awesome for icons. The application will render within a div with the ID app.
Setup .NET API project
dotnet new webapi -o api -n AppCreate a testing database named "example" and execute the database.sql file to import the table and data.
.NET API Project structure
├─ Controllers
│ └─ ProductController.cs
├─ Models
│ ├─ DataContext.cs
│ └─ Product.cs
├─ Program.cs
├─ App.csproj
└─ appsettings.json
.NET API Project files
App.csproj
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Web">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>net8.0</TargetFramework>
<ImplicitUsings>enable</ImplicitUsings>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="MySql.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="8.0.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>This file is the .NET project configuration file, where we have added the MySql.EntityFrameworkCore package.
appsettings.json
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Database": "server=localhost;port=3306;database=example;user id=root;password=;"
}
}This is the .NET application configuration file, which includes the database connection details.
Program.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddDefaultPolicy(policy => {
policy.AllowAnyOrigin();
policy.AllowAnyHeader();
policy.AllowAnyMethod();
});
});
builder.Services.AddDbContext<App.Models.DataContext>(options => options.UseMySQL(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("Database")));
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseCors();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();The program.csfile is the main entry point for the .NET application. It configures services, sets up CORS, establishes a MySQL database context, and defines middleware for routing before starting the application.
DataContext.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace App.Models
{
public partial class DataContext : DbContext
{
public virtual DbSet<Product> Product { get; set; }
public DataContext()
{
}
public DataContext(DbContextOptions<DataContext> options) : base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Product>(entity =>
{
entity.ToTable("Product");
entity.HasKey(e => e.Id);
entity.Property(e => e.Id).HasColumnName("id");
entity.Property(e => e.Name).HasColumnName("name").HasMaxLength(50).IsUnicode(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Price).HasColumnName("price").HasColumnType("decimal(12,2)");
});
}
}
}DataContext.cs defines the Entity Framework Core context for the application, featuring a DbSetProduct table. It also sets up the Product entity with table mapping, primary key, and column details, including names, types, and constraints.
Product.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace App.Models
{
public class Product
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}Product.cs defines the model that maps to the database table named Product. It includes properties with annotations that specify how these properties correspond to the table's columns.
ProductController.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using App.Models;
namespace App.Controllers
{
public class ProductController : Controller
{
private readonly DataContext _context;
public ProductController(DataContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
[HttpGet("api/products")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Index()
{
var products = await _context.Product.ToListAsync();
return Ok(products);
}
[HttpGet("api/products/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Detail(int? id)
{
var product = await _context.Product.FirstOrDefaultAsync(e => e.Id == id);
return Ok(product);
}
[HttpPost("api/products")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create([FromBody] Product model)
{
var product = new Product();
product.Id = model.Id;
product.Name = model.Name;
product.Price = model.Price;
_context.Add(product);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(product);
}
[HttpPut("api/products/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Update(int id, [FromBody] Product model)
{
var product = await _context.Product.FirstOrDefaultAsync(e => e.Id == id);
product.Name = model.Name;
product.Price = model.Price;
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok(product);
}
[HttpDelete("api/products/{id}")]
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(int id)
{
var product = await _context.Product.FindAsync(id);
_context.Product.Remove(product);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return Ok();
}
}
}The ProductController class provides API endpoints for managing Product entities. It uses DataContext to interact with the database:
Index(GET) retrieves all products.Detail(GET) fetches a specific product by ID.Create(POST) adds a new product.Update(PUT) modifies an existing product by ID.Delete(DELETE) removes a product by ID.
Run projects
Run Vue project
npm run devRun .NET API project
dotnet runOpen the web browser and goto http://localhost:5173
You will find this product list page.
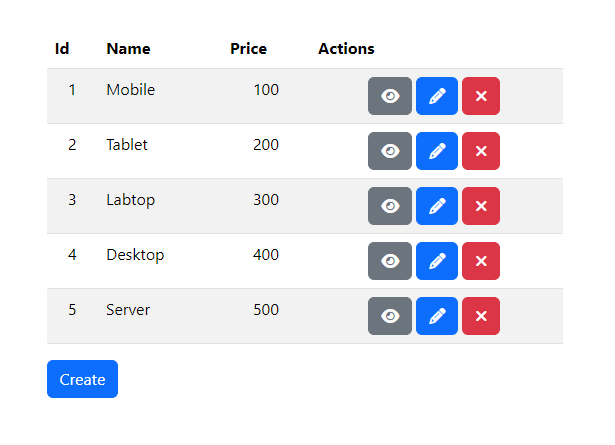
Testing
Click the "View" button to see the product details page.
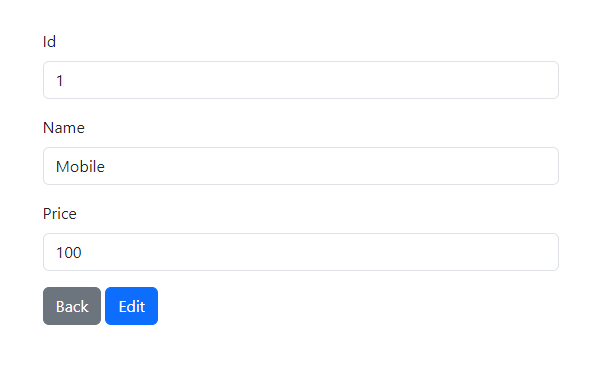
Click the "Edit" button to modify the product and update its details.
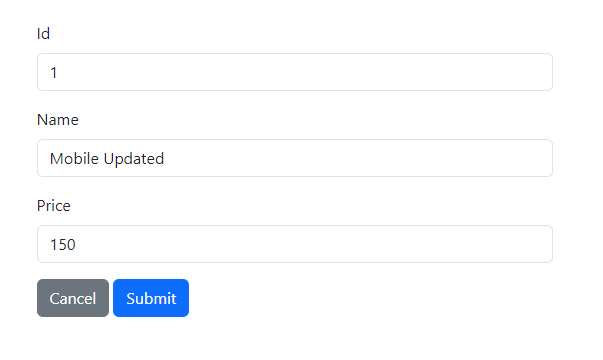
Click the "Submit" button to save the updated product details.
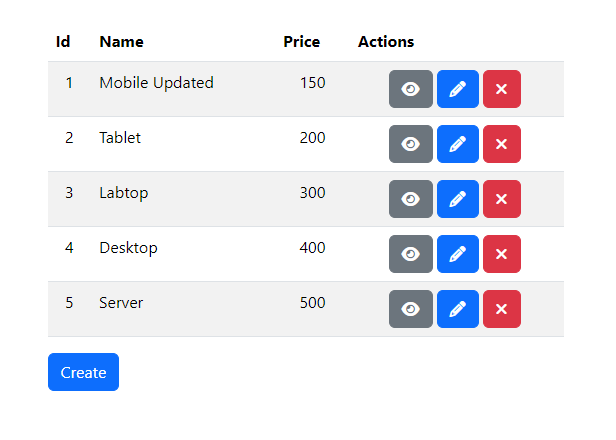
Click the "Create" button to add a new product and input its details.
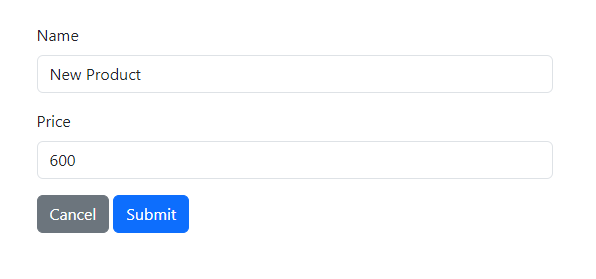
Click the "Submit" button to save the new product.
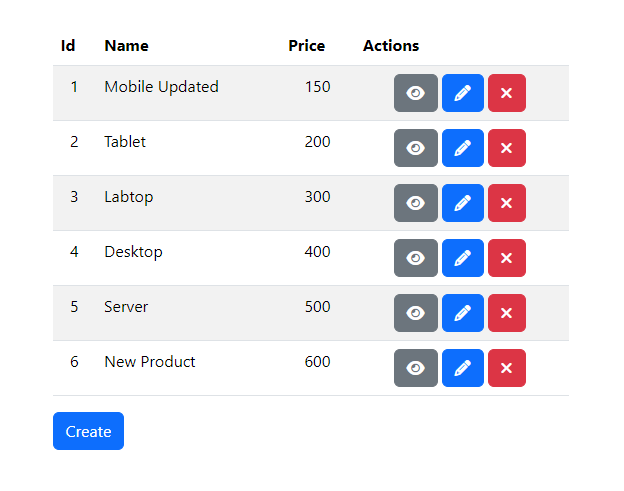
Click the "Delete" button to remove the previously created product.
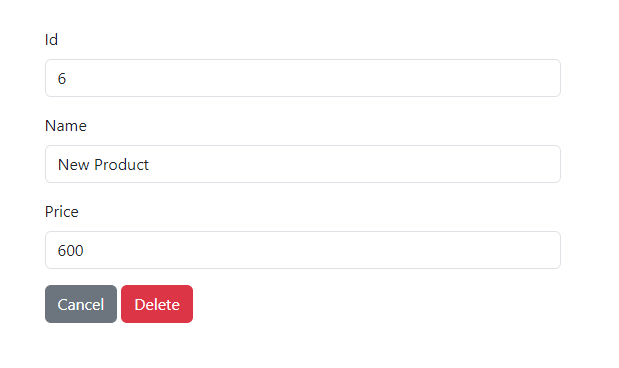
Click the "Delete" button to confirm the removal of this product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned how to create a basic Vue project using Single-File Components (SFC) to build views and define application routing. By integrating with a .NET API as the backend and utilizing Entity Framework for database operations, we've developed a dynamic front-end that effectively communicates with a robust backend, providing a solid foundation for modern, full-stack web applications.
Source code: https://github.com/stackpuz/Example-CRUD-Vue-3-dotnet-8
Create a Vue CRUD App in Minutes: https://stackpuz.com