Building an Angular CRUD App with a FastAPI
CRUD operations are at the core of many web applications. This article will take you through the process of developing a CRUD app with Angular for the front end and an Express API for the back end, illustrating how these frameworks work together to create a cohesive full-stack application.
Prerequisites
- Node.js
- Python 3.10
- MySQL
Setup Angular project
Install Angular 18 and create a new project with the following command.
npm install -g @angular/cli@18.0.0
ng new view --minimal --routing --style css --no-standalone --ssr=falseAngular project structure
└─ src
├─ app
│ ├─ app-routing.module.ts
│ ├─ app.component.ts
│ ├─ app.interceptor.ts
│ ├─ app.module.ts
│ └─ components
│ └─ product
│ ├─ Create.component.ts
│ ├─ Delete.component.ts
│ ├─ Detail.component.ts
│ ├─ Edit.component.ts
│ ├─ Index.component.ts
│ └─ Product.service.ts
├─ index.html
├─ main.ts
└─ styles.css*This project structure will display only the files and folders that we plan to create or modify.
Angular Project files
main.ts
import { enableProdMode } from '@angular/core'
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from '@angular/platform-browser-dynamic'
import { AppModule } from './app/app.module'
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule).catch(e => console.error(e))This main.ts file initializes an Angular application by bootstrapping the AppModule using the platformBrowserDynamic function. It sets up the application to run in the browser and handles any errors that occur during the bootstrapping process.
app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'
import { HttpClientModule, HTTP_INTERCEPTORS } from '@angular/common/http'
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module'
import { AppComponent } from './app.component'
import { AppInterceptor } from './app.interceptor'
import { ProductIndex } from './components/product/Index.component'
import { ProductCreate } from './components/product/Create.component'
import { ProductDetail } from './components/product/Detail.component'
import { ProductEdit } from './components/product/Edit.component'
import { ProductDelete } from './components/product/Delete.component'
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
ProductIndex,
ProductCreate,
ProductDetail,
ProductEdit,
ProductDelete,
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule,
FormsModule,
HttpClientModule
],
providers: [
{ provide: HTTP_INTERCEPTORS, useClass: AppInterceptor, multi: true }
],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }The AppModule is the main module of an Angular application. It imports core Angular modules and sets up routing with AppRoutingModule. The module declares various product-related components. It also registers AppInterceptor as an HTTP interceptor. The AppComponent is set as the bootstrap component, making it the entry point of the application.
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
template: `<router-outlet></router-outlet>`
})
export class AppComponent { }The app.component.ts file defines the root component, AppComponent, which uses the <router-outlet>app-root selector and serves as the entry point for the Angular application.
app.interceptor.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HttpInterceptor } from '@angular/common/http';
import { HttpRequest, HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http'
import { Observable, throwError } from 'rxjs'
import { HttpHandler } from '@angular/common/http'
import { HttpEvent } from '@angular/common/http'
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class AppInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
baseURL = 'http://localhost:8000/api'
intercept(request: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
return next.handle(request.clone({
url: this.baseURL + request.url,
}))
}
}The AppInterceptor class is an Angular HTTP interceptor that appends a configurable baseURL to all outgoing HTTP request URLs before they are sent to the server. This allows the application to centralize and easily manage the base API endpoint.
app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductIndex } from './components/product/Index.component'
import { ProductCreate } from './components/product/Create.component'
import { ProductDetail } from './components/product/Detail.component'
import { ProductEdit } from './components/product/Edit.component'
import { ProductDelete } from './components/product/Delete.component'
const routes: Routes = [
{ path: '', redirectTo: 'product', pathMatch: 'full' },
{ path: 'product', component: ProductIndex },
{ path: 'product/create', component: ProductCreate },
{ path: 'product/:id', component: ProductDetail },
{ path: 'product/edit/:id', component: ProductEdit },
{ path: 'product/delete/:id', component: ProductDelete }
]
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }The AppRoutingModule sets up routing for an Angular application, including product-related paths for listing, creating, viewing, editing, and deleting products. It also includes a route that redirects from the root path "/" to the product listing page "/product".
Create.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductService } from './Product.service'
@Component({
selector: 'product-create',
template: `
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form ngNativeValidate method="post" (submit)="create()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input id="product_name" name="name" class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="product.name" maxlength="50" />
<span *ngIf="errors.name" class="text-danger">{{errors.name}}</span>
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input id="product_price" name="price" class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="product.price" type="number" />
<span *ngIf="errors.price" class="text-danger">{{errors.price}}</span>
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<a class="btn btn-secondary" routerLink="/product">Cancel</a>
<button class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>`
})
export class ProductCreate {
product?: any = {}
errors?: any = {}
constructor(private router: Router, private route: ActivatedRoute, private ProductService: ProductService) { }
create() {
this.ProductService.create(this.product).subscribe(() => {
this.router.navigateByUrl('/product')
}, (e) => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
}The ProductCreate component provides a form for creating a new product, binding input fields for name and price to a product object. On submission, it calls ProductService to create the product and navigates back to the product list. Validation errors are displayed next to the corresponding fields, and any creation errors trigger an alert.
Delete.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductService } from './Product.service'
@Component({
selector: 'product-delete',
template: `
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form ngNativeValidate method="post" (submit)="this.delete()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="id" class="form-control" value="{{product.id}}" type="number" required />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input readonly id="product_name" name="name" class="form-control" value="{{product.name}}" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input readonly id="product_price" name="price" class="form-control" value="{{product.price}}" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<a class="btn btn-secondary" routerLink="/product">Cancel</a>
<button class="btn btn-danger">Delete</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>`
})
export class ProductDelete {
product?: any = {}
constructor(private router: Router, private route: ActivatedRoute, private ProductService: ProductService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.get()
}
get() {
return this.ProductService.delete(this.route.snapshot.params['id']).subscribe(data => {
this.product = data
}, e => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
delete() {
this.ProductService.delete(this.route.snapshot.params['id'], this.product).subscribe(() => {
this.router.navigateByUrl('/product')
}, (e) => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
}The ProductDelete component in Delete.component.ts is an Angular component that handles the deletion of a product. It displays a form with read-only fields showing the product's details (ID, name, and price). When the component initializes, it fetches the product details using the product ID from the route. On form submission, the delete() method calls ProductService to delete the product and then redirects to the product list. If there's an error during deletion, an alert is shown.
Detail.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductService } from './Product.service'
@Component({
selector: 'product-detail',
template: `
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form ngNativeValidate method="post">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="id" class="form-control" value="{{product.id}}" type="number" required />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input readonly id="product_name" name="name" class="form-control" value="{{product.name}}" maxlength="50" />
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input readonly id="product_price" name="price" class="form-control" value="{{product.price}}" type="number" />
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<a class="btn btn-secondary" routerLink="/product">Back</a>
<a class="btn btn-primary" routerLink="/product/edit/{{product.id}}">Edit</a>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>`
})
export class ProductDetail {
product?: any = {}
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute, private ProductService: ProductService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.get()
}
get() {
return this.ProductService.get(this.route.snapshot.params['id']).subscribe(data => {
this.product = data
}, e => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
}The ProductDetail component displays the details of a specific product. It retrieves the product information based on the ID from the route and shows the product's ID, name, and price in read-only fields. The component provides "Back" and "Edit" buttons for navigation. The product details are fetched and displayed when the component initializes.
Edit.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
import { ActivatedRoute, Router } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductService } from './Product.service'
@Component({
selector: 'product-edit',
template: `
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<form ngNativeValidate method="post" (submit)="edit()">
<div class="row">
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_id">Id</label>
<input readonly id="product_id" name="id" class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="product.id" type="number" required />
<span *ngIf="errors.id" class="text-danger">{{errors.id}}</span>
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_name">Name</label>
<input id="product_name" name="name" class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="product.name" maxlength="50" />
<span *ngIf="errors.name" class="text-danger">{{errors.name}}</span>
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-md-6 col-lg-4">
<label class="form-label" for="product_price">Price</label>
<input id="product_price" name="price" class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="product.price" type="number" />
<span *ngIf="errors.price" class="text-danger">{{errors.price}}</span>
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<a class="btn btn-secondary" routerLink="/product">Cancel</a>
<button class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>`
})
export class ProductEdit {
product?: any = {}
errors?: any = {}
constructor(private router: Router, private route: ActivatedRoute, private ProductService: ProductService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.get()
}
get() {
return this.ProductService.edit(this.route.snapshot.params['id']).subscribe(data => {
this.product = data
}, e => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
edit() {
this.ProductService.edit(this.route.snapshot.params['id'], this.product).subscribe(() => {
this.router.navigateByUrl('/product')
}, (e) => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
}The ProductEdit component allows users to edit an existing product. It retrieves the product details using the product ID from the route and displays them in a form with editable fields for name and price. On form submission, it updates the product via ProductService and navigates back to the product list. Any errors during fetching or updating are shown as alerts, and validation errors are displayed next to the relevant fields.
Index.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core'
import { Router, NavigationEnd } from '@angular/router'
import { ProductService } from './Product.service'
@Component({
selector: 'product-index',
template: `
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Id</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Price</th>
<th>Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr *ngFor="let product of products">
<td class="text-center">{{product.id}}</td>
<td>{{product.name}}</td>
<td class="text-center">{{product.price}}</td>
<td class="text-center">
<a class="btn btn-secondary" routerLink="/product/{{product.id}}" title="View"><i class="fa fa-eye"></i></a>
<a class="btn btn-primary" routerLink="/product/edit/{{product.id}}" title="Edit"><i class="fa fa-pencil"></i></a>
<a class="btn btn-danger" routerLink="/product/delete/{{product.id}}" title="Delete"><i class="fa fa-times"></i></a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<a class="btn btn-primary" routerLink="/product/create">Create</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>`
})
export class ProductIndex {
products?: any[]
constructor(public router: Router, private ProductService: ProductService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.get()
}
get() {
this.ProductService.get().subscribe(data => {
this.products = data
}, e => {
alert(e.error)
})
}
}The ProductIndex component displays a list of products in a table format. It fetches the list of products from ProductService on initialization and shows each product's ID, name, and price, with action buttons for viewing, editing, and deleting each product. It also includes a button to navigate to the product creation page.
Product.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'
import { Observable } from 'rxjs'
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class ProductService {
constructor(private http: HttpClient) { }
get(id?: any): Observable<any> {
if (id) {
return this.http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
else {
return this.http.get('/products' + location.search)
}
}
create(data?: any): Observable<any> {
if (data) {
return this.http.post('/products', data)
}
else {
return this.http.get('/products/create')
}
}
edit(id: any, data?: any): Observable<any> {
if (data) {
return this.http.put(`/products/${id}`, data)
}
else {
return this.http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
}
delete(id: any, data?: any): Observable<any> {
if (data) {
return this.http.delete(`/products/${id}`)
}
else {
return this.http.get(`/products/${id}`)
}
}
}The ProductService uses Angular's HttpClient to perform the relevant HTTP requests for product management. It provides methods to:
get(id?): Fetch product details by ID or a list of products if no ID is provided.create(data?): Create a new product ifdatais provided, otherwise fetch the create product page.edit(id, data?): Update a product by ID ifdatais provided, otherwise fetch product details for editing.delete(id, data?): Delete a product by ID ifdatais provided, otherwise fetch product details for confirmation.
styles.css
.container {
margin-top: 2em;
}
.btn {
margin-right: 0.25em;
}The CSS adjusts the layout by adding space above the container and spacing out buttons horizontally.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bootstrap/5.3.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.5.0/css/all.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
</body>
</html>The HTML serves as the main entry point for an Angular application, including Bootstrap for styling, Font Awesome for icons, and <app-root>
Setup FastAPI project
pip install fastapi sqlalchemy pymysql uvicorn python-dotenvCreate a testing database named "example" and execute the database.sql file to import the table and data.
FastAPI Project structure
├─ .env
└─ app
├─ db.py
├─ main.py
├─ models
│ └─ product.py
├─ routers
│ └─ product.py
├─ schemas
│ └─ product.py
└─ __init__.py
__init__.py is used to mark the directory as a Python package, allowing it to be recognized as a module that can contain submodules and facilitate imports.
FastAPI Project files
.env
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=example
DB_USER=root
DB_PASSWORD=
This file holds the configuration details for connecting to the database.
db.py
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
load_dotenv()
url = f"mysql+pymysql://{os.getenv('DB_USER')}:{os.getenv('DB_PASSWORD')}@{os.getenv('DB_HOST')}:{os.getenv('DB_PORT')}/{os.getenv('DB_DATABASE')}"
engine = create_engine(url)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
Base = declarative_base()
def get_db():
db = SessionLocal()
try:
yield db
finally:
db.close()
The db.py module sets up the database connection for a FastAPI application using SQLAlchemy. It loads database credentials from environment variables, creates a SQLAlchemy engine for a MySQL database, and establishes a session factory for database interactions. The get_db function provides a database session that can be used in dependency injection, ensuring proper session management by closing the session after use.
models\product.py
from sqlalchemy import *
from app.db import Base
class Product(Base):
__tablename__ = "Product"
id = Column(INTEGER, primary_key=True)
name = Column(VARCHAR)
price = Column(DECIMAL)The models\product.py module defines a SQLAlchemy model for the Product table, mapping its columns for the product's ID, name, and price. It extends the Base class from the db module, enabling easy interaction with product data in the database.
schemas\product.py
from pydantic import BaseModel
from decimal import Decimal
class ProductCreate(BaseModel):
name: str
price: Decimal
class ProductUpdate(BaseModel):
name: str
price: Decimal
The schemas/product.py module defines Pydantic models for validating and serializing product data in a FastAPI application. It includes two classes: ProductCreate, which is used for creating new products by specifying the name and price, and ProductUpdate, which is designed for updating existing product information. Both classes ensure that the provided data adheres to the expected types.
routers\product.py
from fastapi import APIRouter, Depends
from sqlalchemy.orm import Session
from app.db import get_db
from app.models.product import Product
from app.schemas.product import ProductCreate, ProductUpdate
router = APIRouter()
@router.get("/products")
def index(db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
return db.query(Product).all()
@router.get("/products/{id}")
def get(id: int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
return db.query(Product).filter(Product.id == id).first()
@router.post("/products")
def create(payload: ProductCreate, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
product = Product(**payload.model_dump())
db.add(product)
db.commit()
db.refresh(product)
return product
@router.put("/products/{id}")
def update(id: int, payload: ProductUpdate, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
product = db.query(Product).filter(Product.id == id).first()
product.name = payload.name
product.price = payload.price
db.commit()
db.refresh(product)
return product
@router.delete("/products/{id}")
def delete(id: int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
db.query(Product).filter(Product.id == id).delete()
db.commit()
The routers/product.py module defines a FastAPI router for managing product-related API endpoints. It provides the following functionalities:
indexfunction returns a list of all products from the database.getfunction fetches a specific product by its ID.createfunction adds a new product to the database using the data provided in theProductCreateschema.updatefunction modifies an existing product's details based on its ID and the providedProductUpdatedata.deletefunction removes a product from the database by its ID.
All operations depend on a database session obtained through the get_db dependency, ensuring proper session management for each request.
main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import FileResponse
from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
from app.routers.product import router
app = FastAPI()
app.include_router(router, prefix="/api")
@app.get("/")
async def read_index():
return FileResponse("app/static/index.html")
app.add_middleware(
CORSMiddleware,
allow_origins=["*"],
allow_methods=["*"],
allow_headers=["*"],
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="127.0.0.1")
The main.py module serves as the entry point for a FastAPI application. It initializes the FastAPI app and includes a router for product-related endpoints under the /api prefix. The module also defines a root endpoint that serves an index.html file from the static directory. CORS middleware is added to allow requests from any origin, enabling cross-origin resource sharing. Finally, the application is configured to run with Uvicorn when executed directly, listening on 127.0.0.1.
Run projects
Run Angular project
npm startRun FastAPI project
uvicorn app.main:app
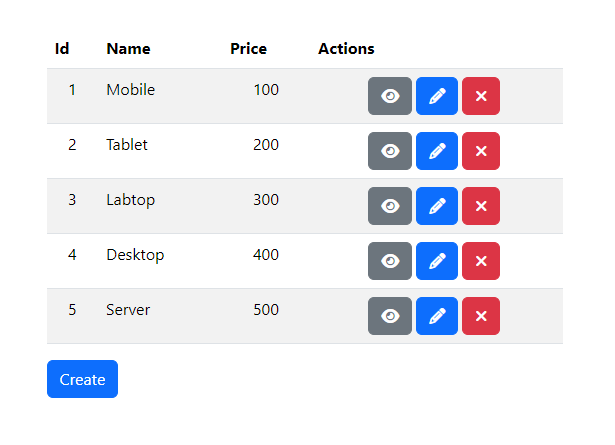
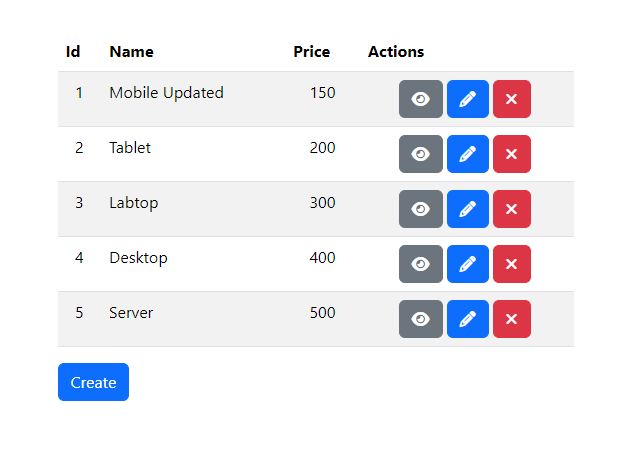
Open the web browser and goto http://localhost:4200
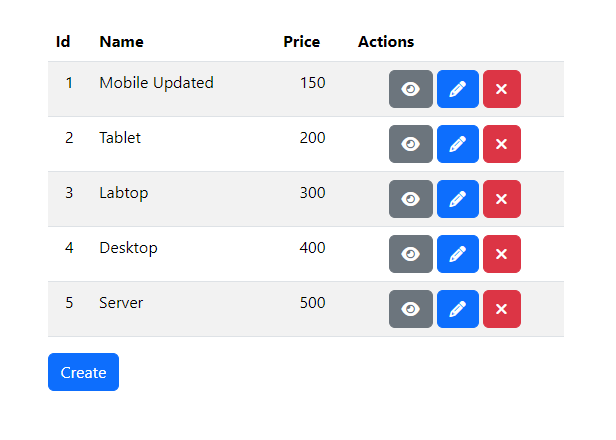
You will find this product list page.
Testing
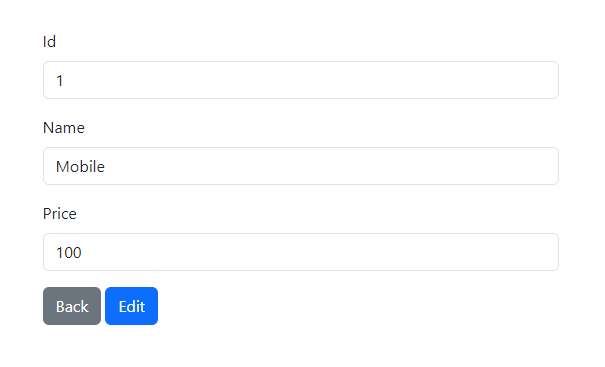
Click the "View" button to see the product details page.
Click the "Edit" button to modify the product and update its details.
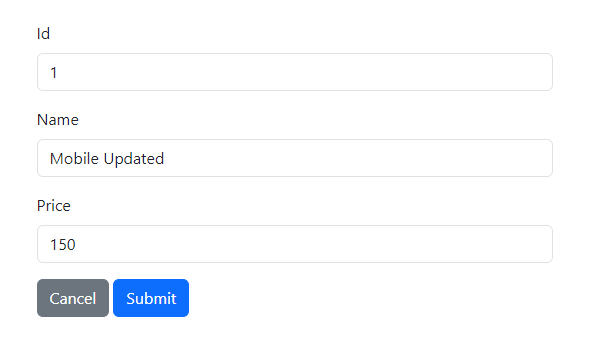
Click the "Submit" button to save the updated product details.
Click the "Create" button to add a new product and input its details.
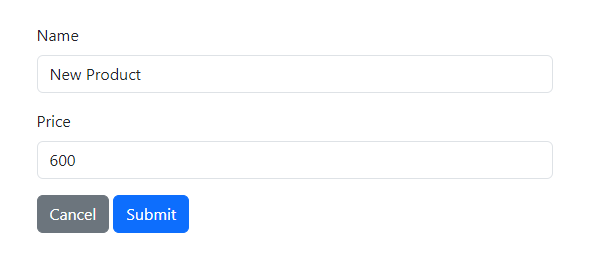
Click the "Submit" button to save the new product.
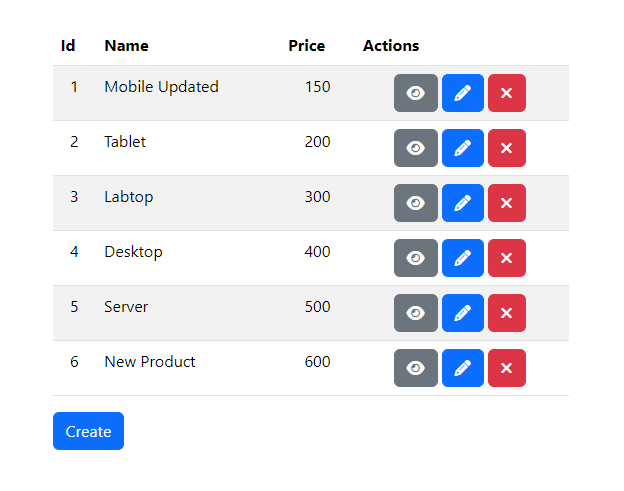
Click the "Delete" button to remove the previously created product.
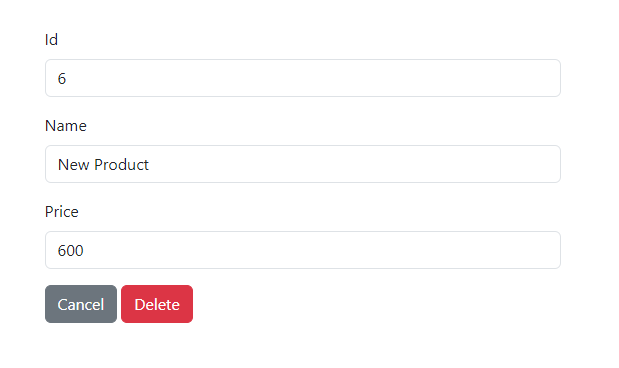
Click the "Delete" button to confirm the removal of this product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have learned how to create a basic Angular project with components, views, and routing, while setting up a FastAPI server as the backend. By using SQLAlchemy for database operations, we built a dynamic front-end that seamlessly interacts with a robust backend. This setup provides a solid foundation for developing modern, full-stack web applications.
Source code: https://github.com/stackpuz/Example-CRUD-Angular-18-FastAPI
Create an Angular CRUD App in Minutes: https://stackpuz.com